Load gnss_lib_py into the Python workspace
[1]:
import gnss_lib_py as glp
CLK File Parsing
This tutorial shows how to load CLK files.
[2]:
# download an example .clk data file
glp.make_dir("../data")
!wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Stanford-NavLab/gnss_lib_py/main/data/unit_test/clk/COD0MGXFIN_20211180000_01D_30S_CLK.CLK --quiet -nc -O "../data/COD0MGXFIN_20211180000_01D_30S_CLK.CLK"
# Specify .clk file path to extract precise ephemerides
clk_path = "../data/COD0MGXFIN_20211180000_01D_30S_CLK.CLK"
Use the Clk class loader to load in the CLK file. The class can also optionally take multiple files as a list.
[3]:
clk = glp.Clk(clk_path)
clk
[3]:
gps_millis gnss_sv_id gnss_id sv_id b_sv_m
0 1.303673e+12 C06 beidou 6 97992.568020
1 1.303673e+12 C07 beidou 7 -50292.557148
2 1.303673e+12 C08 beidou 8 -267030.259435
3 1.303673e+12 C09 beidou 9 168575.241728
4 1.303673e+12 C10 beidou 10 -15008.617041
... ... ... ... ... ...
14031 1.303677e+12 R19 glonass 19 -42455.802968
14032 1.303677e+12 R20 glonass 20 -14437.014343
14033 1.303677e+12 R21 glonass 21 -61485.194711
14034 1.303677e+12 R22 glonass 22 -33007.363219
14035 1.303677e+12 R24 glonass 24 12180.261592
[5 rows x 14036 columns]
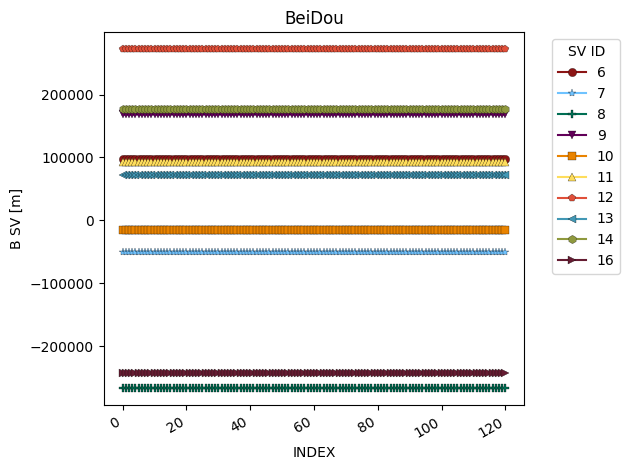
To visualize the results, we’ll plot the clock bias of the first BeiDou satellites.
[4]:
clk_first_beidou = clk.where("gnss_id","beidou").where("sv_id",16,"leq")
fig = glp.plot_metric_by_constellation(clk_first_beidou,"b_sv_m")